Site card
LIFT and Hybrid Micro-manufacturing Laboratory
Where:
Laser Centre
Ubicación:
90A.00.016.1 y 90A.00.017.0, Centro Láser
Typology:
Infraestructura Científica
Manager: Miguel Morales
Email:
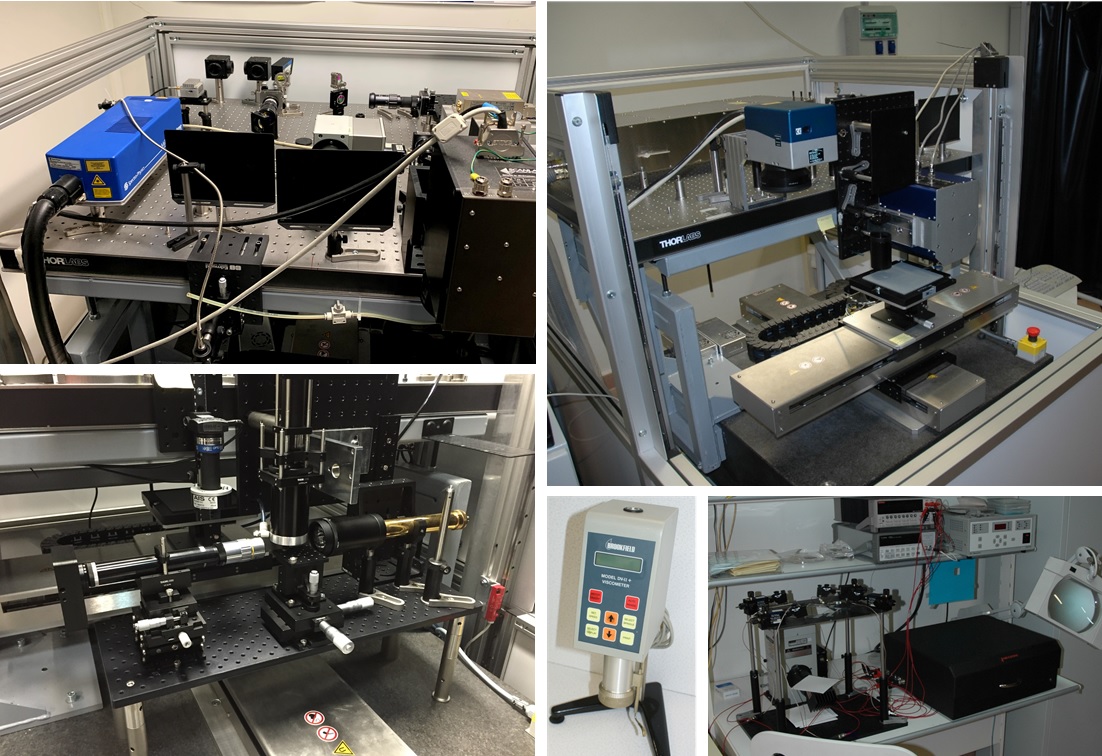
Workstation for carrying out laser direct-write processes, especially laser-induced forward transfer (LIFT), for additive and surface-modification laser printing processes. It also allows additive and subtractive processes to be combined with micrometric resolution. For this purpose, the system combines laser sources with different wavelengths and pulse durations with beam positioning systems (optical fibre, scanners and even a variable-focus optoacoustic system), sample positioning systems (positioning axes) and process characterisation (including ultra-fast vision systems, viscometers, an optical contact-angle and surface tension measurement system, electrical characterisation, etc.).
Micro-manufacturing, nano-manufacturing, laser processing of materials, additive manufacturing.
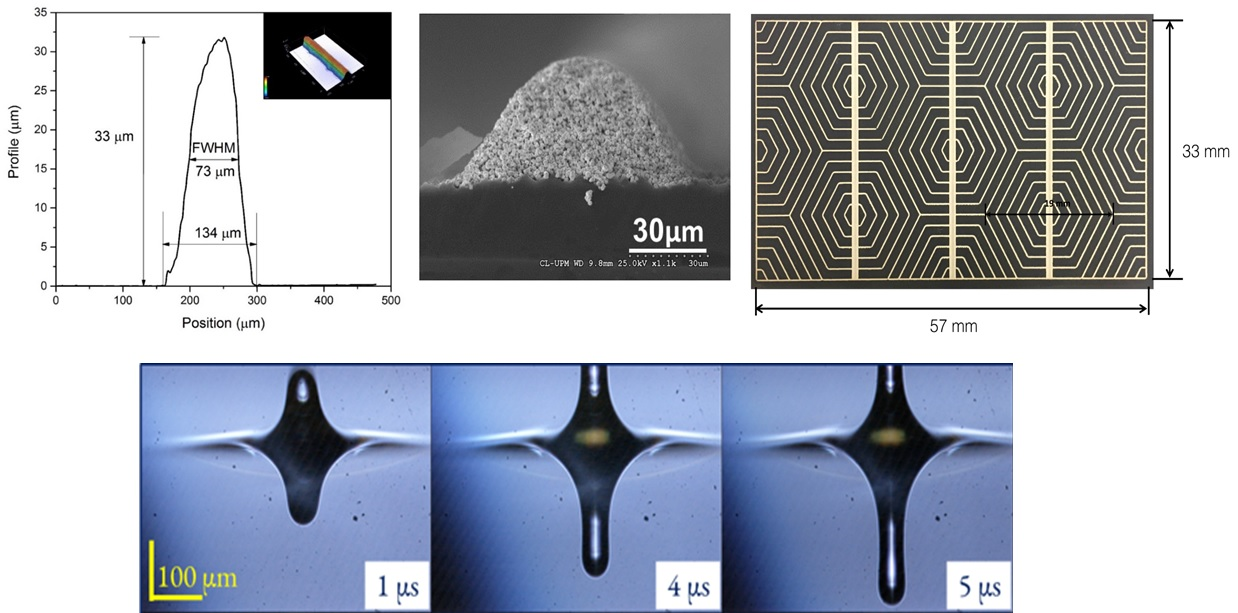
It allows various laser direct-write processes to be carried out, especially LIFT processes, using different laser sources and systems for guiding the beam and moving the sample with micrometric precision, or incorporating vision and process characterisation systems. In the case of additive applications, it is used to deposit material by laser in order to print conductive lines for applications in photovoltaics or flexible electronics and to print with dielectric or insulating ceramic materials. Moreover, it is also possible to carry out thermal surface modification processes, such as the curing and synterisation of previously deposited materials. Combining the above techniques, it is possible to manufacture complete and functional electronic devices and combine that with subtractive applications, such as the selective removal of material by laser ablation, and processes to generate residual stresses, using ps-LSP shock waves, etc.
LIFT metallisation processes, improving the mechanical properties of additive manufacturing samples using shock waves generated with ultra-fast pulses, printing conductive lines for applications in photovoltaics and flexible electronics, printing dielectric and insulating ceramic materials, curing materials, etc.
One of the technological challenges which the machinery manufacturing sector has to face is the development of hybrid technologies combining additive and subtractive processes to achieve a more efficient use of resources and greater speed in the manufacture of complex elements. Specifically, laser-based additive manufacturing (AM) processes can be combined with other laser direct-write techniques such as micro-machining or surface modification, giving rise to hybrid manufacturing processes based on photonic tools.